Gradio's CORS configuration is designed to protect internally deployed applications from attack vectors such as CSRF and data exfiltration attacks originating from external sources. However, the current implementation contains flaws that allow malicious actors to bypass the CORS origin validation, fixed at CVE-2024-47165. This vulnerability can be exploited to steal sensitive data from internally deployed Gradio applications, even when they are intended to be protected against such attacks.
- Status: Assigned
- CVE: CVE-2025-5320
Gradio <= 5.6.0
This vulnerability could allow unauthorized access to sensitive data from internal applications, posing significant risks in scenarios where Gradio is used for sensitive data processing or hosting secure applications.
Gradio utilizes the is_valid_origin method to determine the validity of incoming cross-origin requests. The method aims to block cross-origin requests for locally deployed applications by verifying if the Host header matches the predefined localhost_aliases.
- Localhost Identification:
- Gradio differentiates between locally deployed applications and public-facing ones by comparing the request
Hostheader withlocalhost_aliases(e.g.,127.0.0.1,localhost). If a match is found, Gradio blocks cross-origin requests unless theOriginheader matcheslocalhost_aliases.
- Gradio differentiates between locally deployed applications and public-facing ones by comparing the request
- Inherent Trust for Non-Local Applications:
- When the application is deemed public-facing (not matching
localhost_aliases), Gradio allows all cross-origin requests without verifying the origin. This creates an unintended trust relationship.
- When the application is deemed public-facing (not matching
-
Attackers can exploit this flawed defensive mechanism by manipulating the target URL to bypass the origin validation in at least two ways:
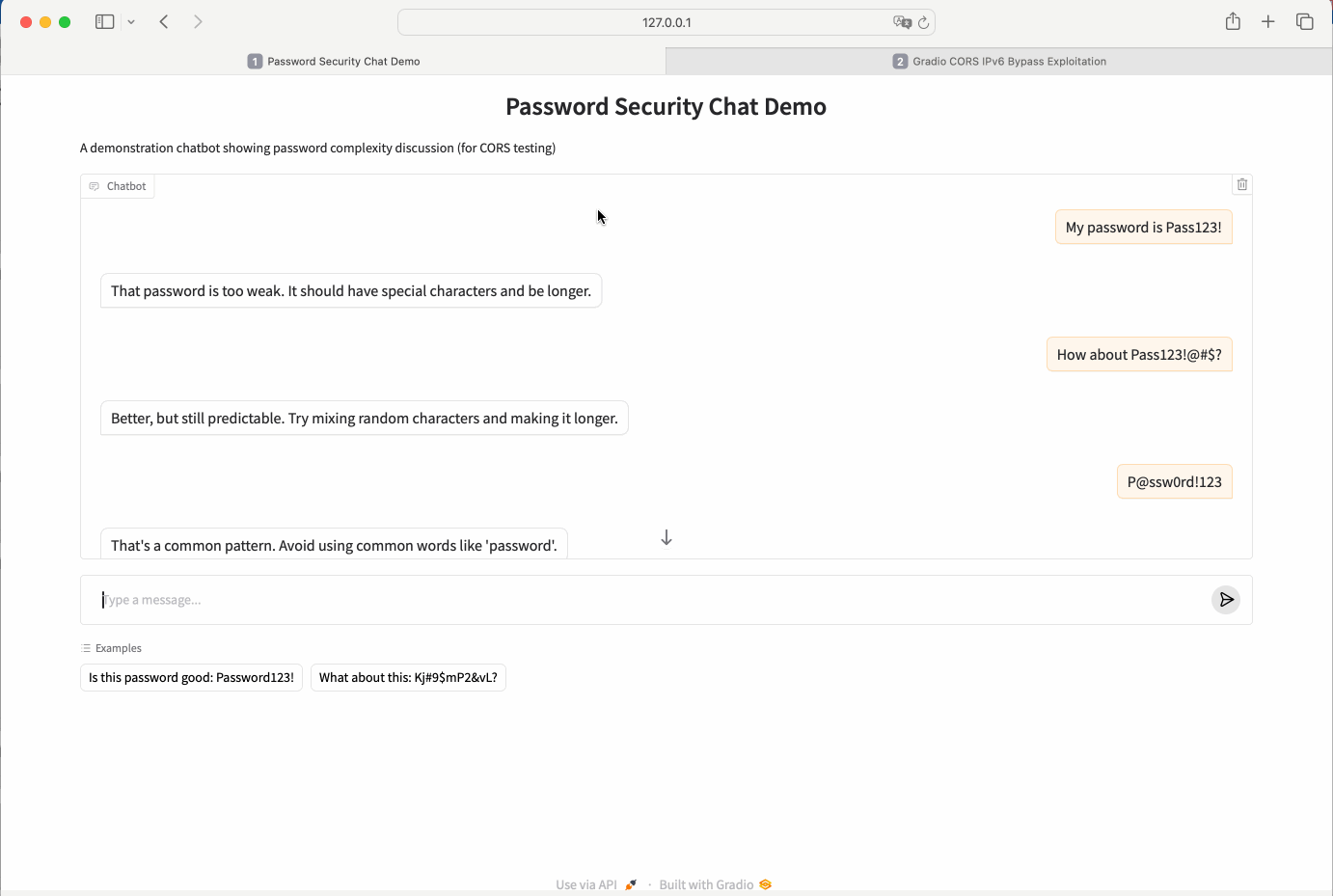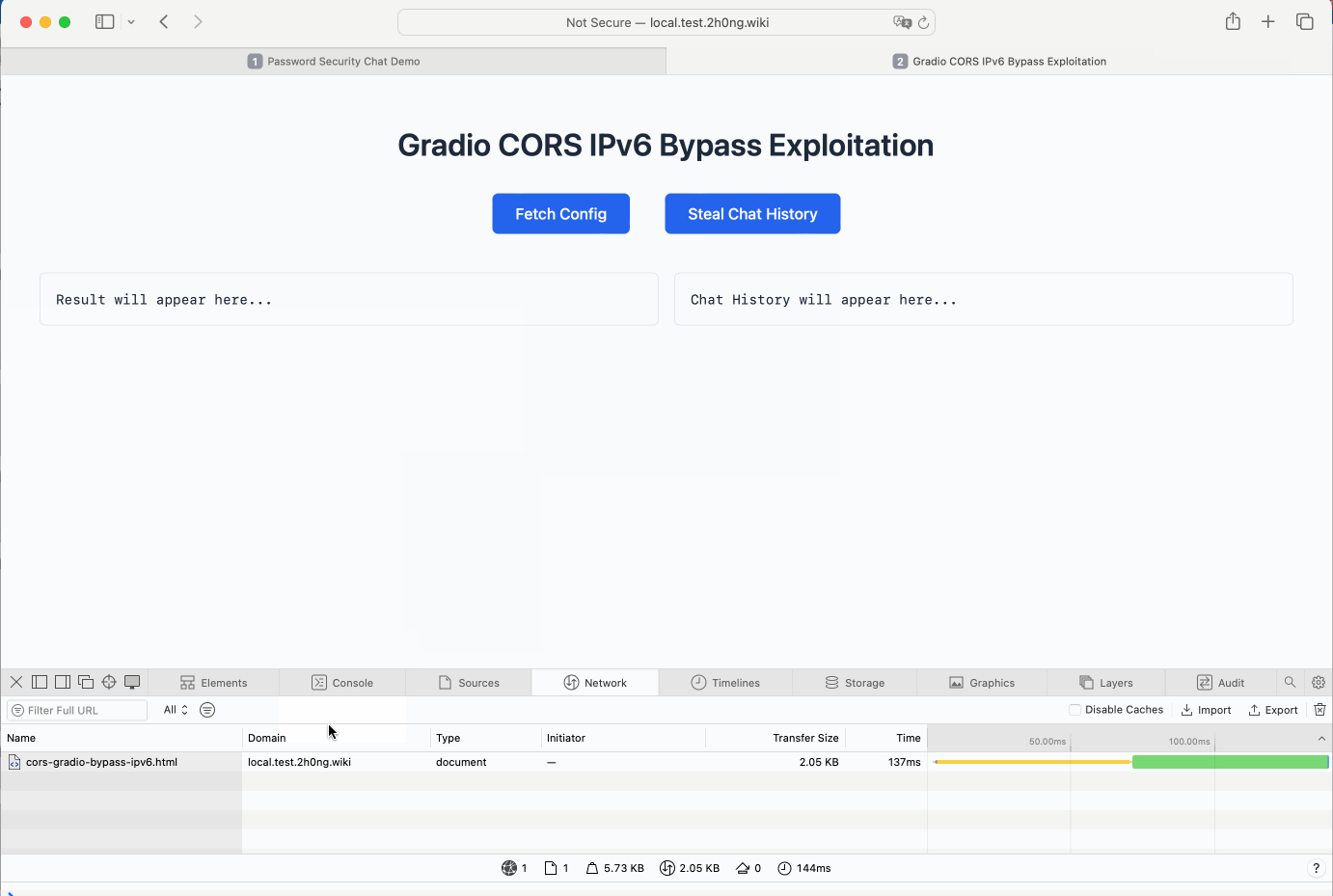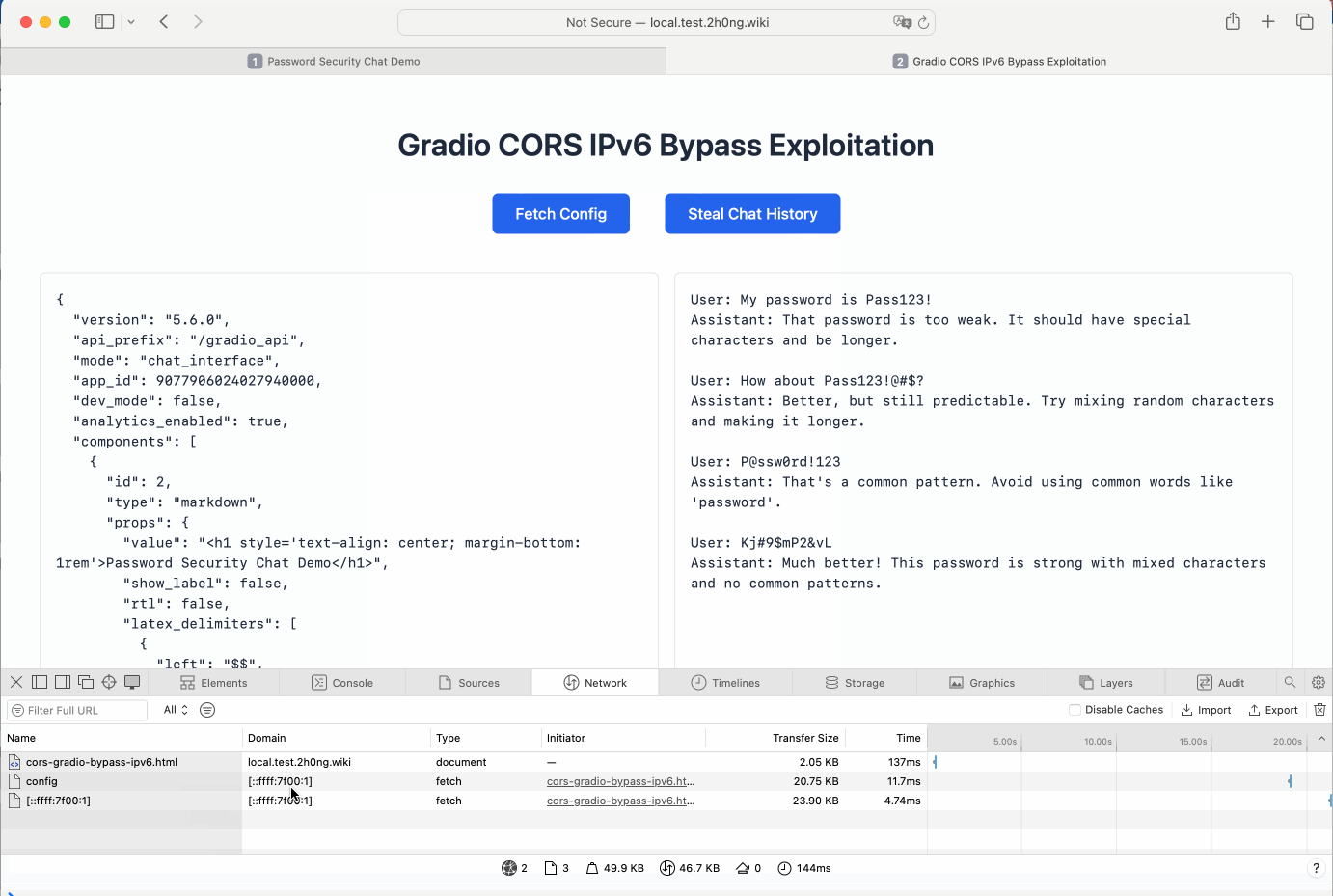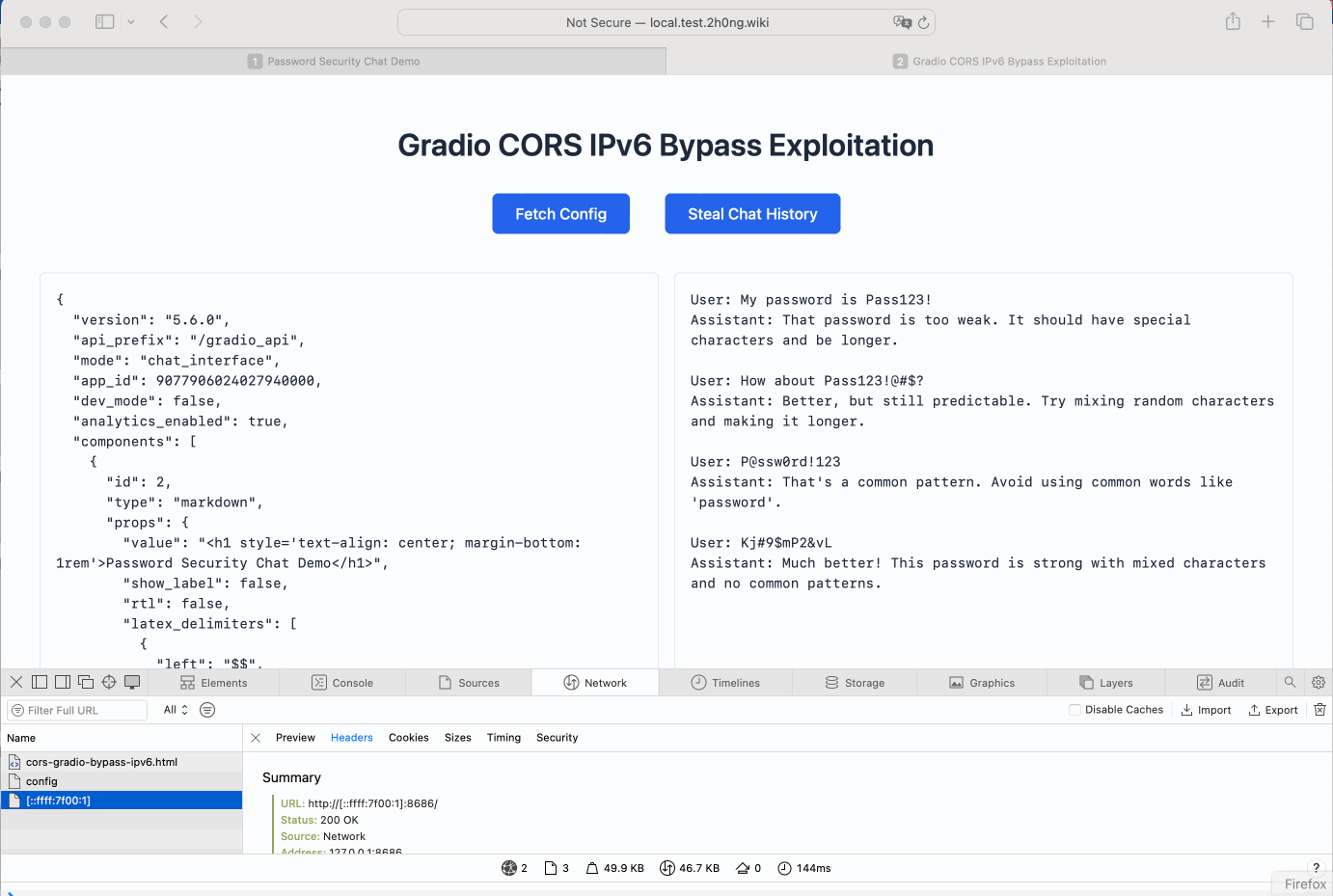
- IPv6 Address Exploitation:
- Requests made to
http://[::ffff:7f00:1]:PORT/bypass the origin check because IPv6 addresses mapped to localhost are not accounted for inlocalhost_aliases.
- Requests made to
- Public Domain Resolving to Localhost:
- By using a public domain that resolves to localhost, such as
http://127.0.0.1.nip.io:PORT/, attackers can bypass the validation logic and send unauthorized cross-origin requests.
- By using a public domain that resolves to localhost, such as
- IPv6 Address Exploitation:
-
Deploy a demo Gradio app:
- Use the provided Gradio demo script to host an application locally at
127.0.0.1:8686.
python3 gradio.demo.py
- Use the provided Gradio demo script to host an application locally at
-
Deploy exploitation payloads on a different origin:
- Use the following exploitations to demonstrate the bypass:
-
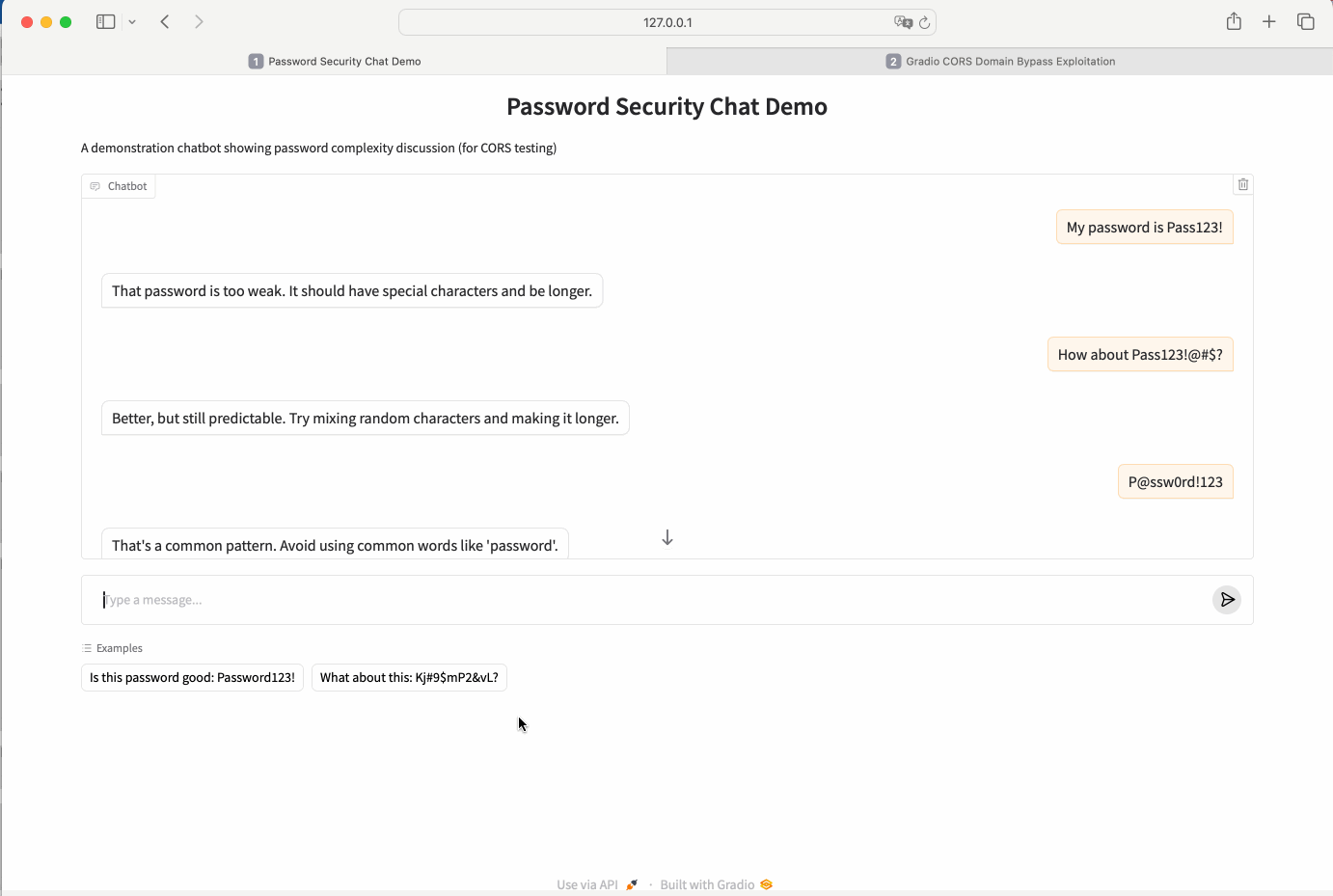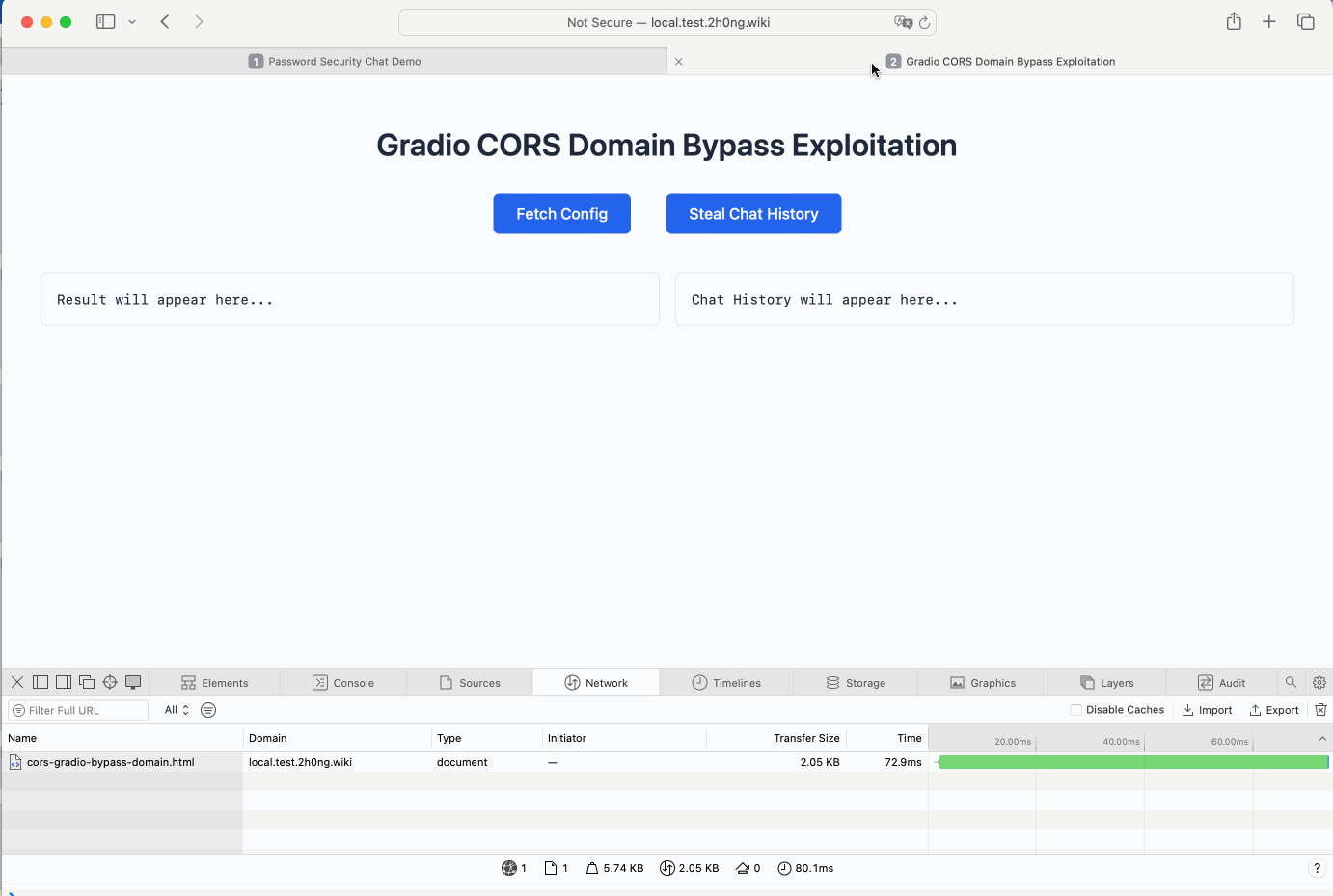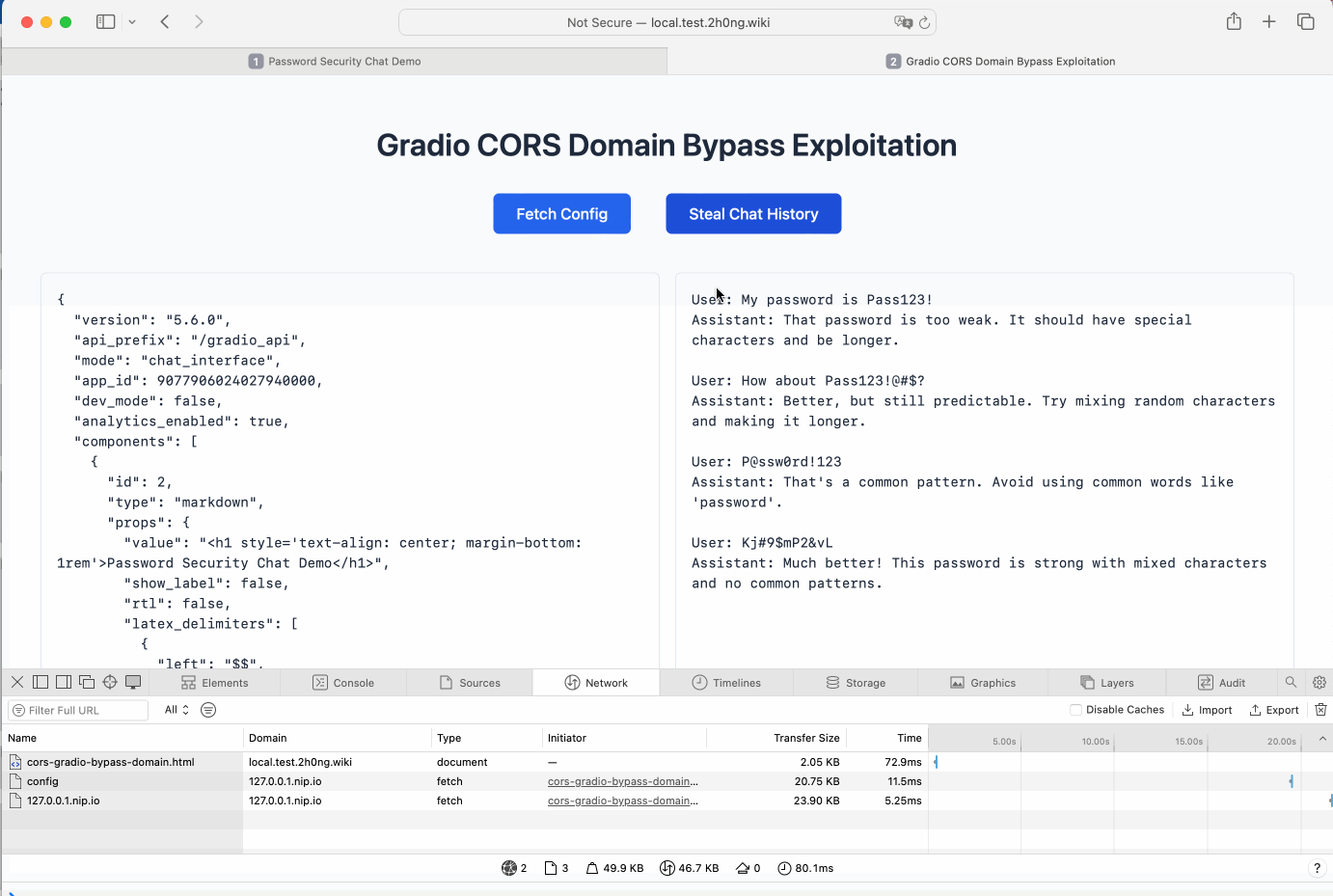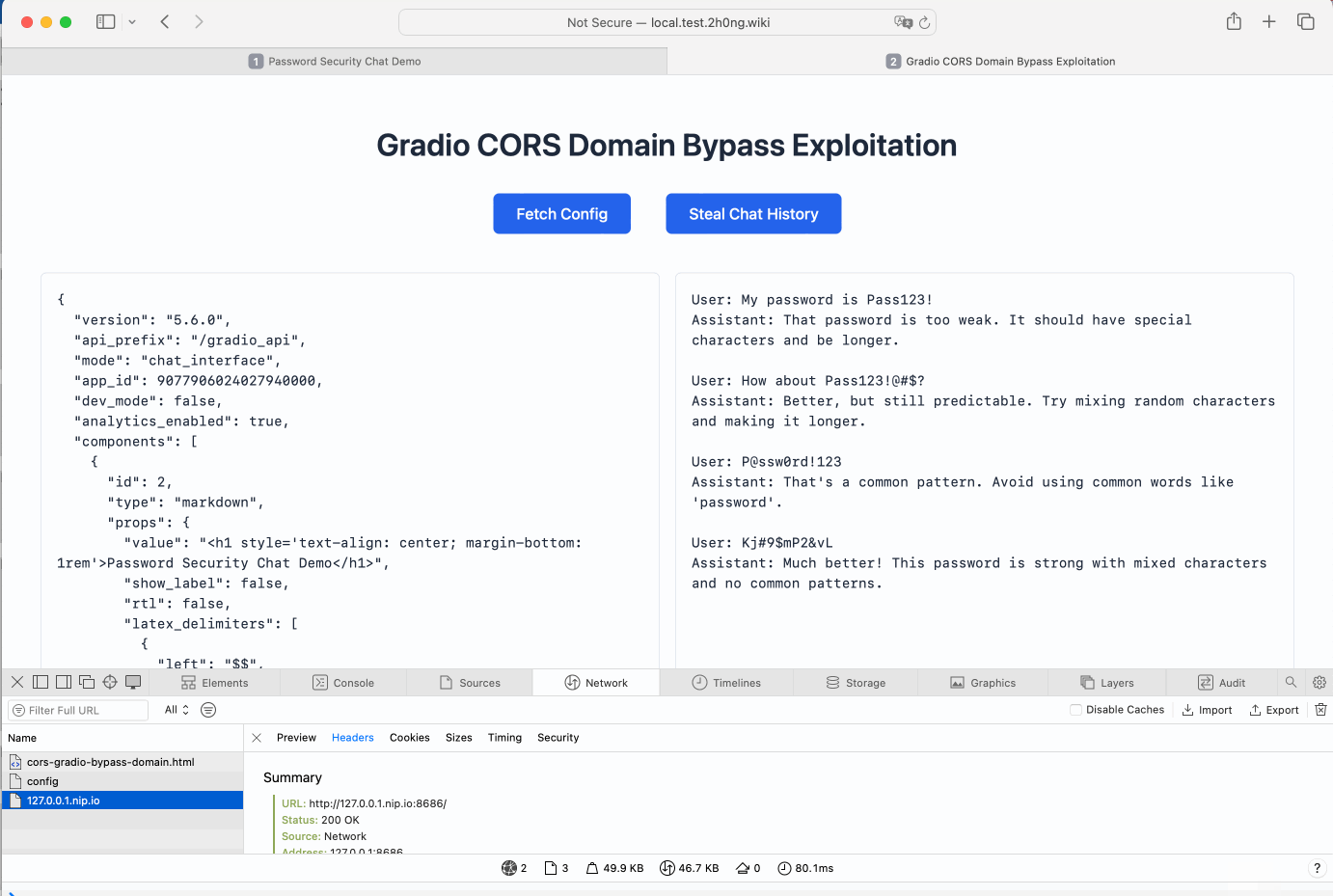
Perform the attack:
- Trigger the exploit by clicking the buttons on the exploitation pages. The actions mimic a malicious actor exfiltrating sensitive data from the internal application.
The demonstration shows that both methods successfully bypass Gradio's CORS restrictions, allowing cross-origin requests to access data from the internal environment.
(Gradio CORS IPv6 Bypass)
(Gradio CORS Domain Bypass)
- Enhance Origin Validation:
- Add support for validating public domains that resolve to internal network. For example, resolves the Host header to determine if the IP address belongs to internal IP address.
- Restrict CORS Policies for Public Deployments:
- Enforce restrictive CORS rules for public-facing Gradio applications, specifying trusted origins explicitly. For example, enforce a whitelist-based origin validation approach for cross origin requests to public-facing applications.
- Update Gradio Documentation:
- Clearly document the risks associated with using the current CORS configuration and provide guidelines for secure deployments.