Created
January 18, 2026 11:55
-
-
Save marklin-latte/034d311933e366b6e2f5e1271f8393ba to your computer and use it in GitHub Desktop.
test
This file contains hidden or bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
|  | |
| 在上一篇文中,我們有從這篇論文中有提到兩種 RAG Post-Retrieval 的主要方向分別為 : | |
| - Reranking | |
| - Context Compressing | |
| [Retrieval-Augmented Generation for Large Language Models: A Survey](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2312.10997) | |
| 然後接下來我們就要說說 `Context Compressing` 的手法。 | |
| # 🚀 Context Compressing 的手法 | |
| > 不是把 retrieve 出來的 document 原封不動返回,而是根據該查詢的脈絡對它們進行壓縮,只回傳與查詢相關的資訊 | |
| 上面這是整個 Context Compressing 的思想核心,然後相關手法事實上很多,我們可以參考這份論文 : | |
| [Contextual Compression in Retrieval-Augmented Generation for Large Language Models: A Survey](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2409.13385) | |
| 主要可以分為以下幾大類與核心概念 : | |
| - Semantic Compression : 在我們將 Contexts ( 就我們第一次 retrive 的結果 ) 丟給 LLM,會先根據語意來進行壓縮。 | |
| - Pre-Trained Language Models : 訓練專門的模型架構來「學會壓縮」。 | |
| - Retrievers : 在 retrieve 階段就過濾掉無關資訊。 | |
| 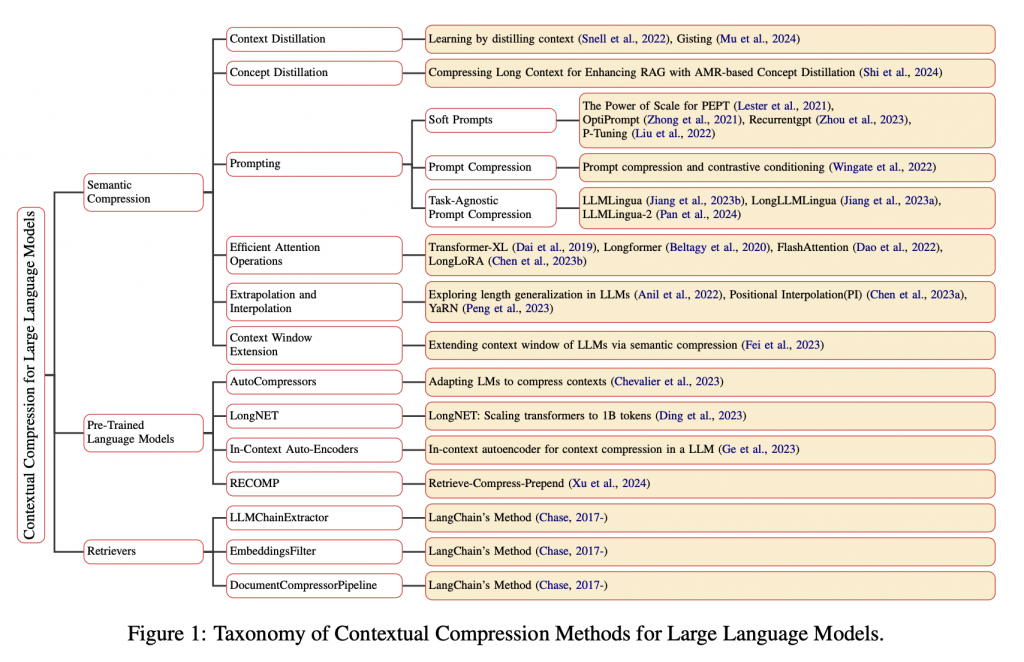 | |
| [圖片來源: Contextual Compression in Retrieval-Augmented Generation for Large Language Models: A Survey](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2409.13385) | |
| 然後這裡我請 GPT 幫我整理成表格,方便之後查詢,有簡單的檢查一下,應該是沒和原文差太多。 | |
| **`Semantic Compression ( AI 產 )`** | |
| | 方法/子類 | 代表論文/實作 | 核心想法 | 何時使用 | 代價/限制 | 工程備註 | | |
| | -------------------------------------------- | ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | -------------------------------- | -------------- | ---------- | ---------------------------------------- | | |
| | Context Distillation | Snell 2022;Mu 2024(Gisting) | 以練習題/思維鏈微調,或把長指令壓成少量 gist tokens | 長提示固定、希望縮短提示成本 | 需資料與微調流程 | 先用 CoT 產教師樣本→微調學生;或用 gist tokens 當 KV 前綴 | | |
| | Concept Distillation | Shi 2024(AMR-based) | 以語義概念圖(AMR)壓縮長上下文 | RAG 長文、多義詞多 | 構建/更新概念圖成本 | 適合知識庫有明確關係圖 | | |
| | Prompting → Soft Prompts/PEFT | Lester 2021;Zhong 2021;Zhou 2023;Liu 2022 | 冻結主模型,只訓練少量前綴/嵌入 | 多任務、少參數調整 | 每任務要維護前綴 | 一任務一前綴;可與檢索器聯動 | | |
| | Prompting → Prompt Compression | Wingate 2022 | 用軟提示擬合原上下文分佈以取代原文 | 有穩定上下文樣板 | 新上下文需再優化 | 對常見長上下文先離線壓縮 | | |
| | Prompting → Task-Agnostic Prompt Compression | Jiang 2023b(LLMLingua)、Jiang 2023a(LongLLMLingua)、Pan 2024(LLMLingua-2) | 以 token 保留/丟棄分類壓縮提示 | 想自動壓縮一般提示 | 需標註/蒐集壓縮資料 | 設保留率與忠實度門檻,壓縮後跑評測 | | |
| | Efficient Attention Operations | Dai 2019(Transformer-XL)、Beltagy 2020(Longformer)、Dao 2022(FlashAttention)、Chen 2023b(LongLoRA) | 以稀疏/重計算/低秩微調降複雜度 | 受上下文限制、需吞吐 | 需替換算子/再訓練 | 先用 FlashAttention;長窗可試 LongLoRA | | |
| | Extrapolation & Interpolation | Anil 2022;Chen 2023a(PI);Peng 2023(YaRN) | 透過位置編碼變換延長可用上下文 | 想快速擴窗不改架構 | 遠距依賴可能降 | 先試 PI,再視需要用 YaRN | | |
| | Context Window Extension | Fei 2023 | 聚類→主題重寫→重組,6–8× 壓縮後再餵模型 | QA/摘要等長文任務 | 前處理複雜 | 建主題粒度與重寫策略,保留可追溯片段 | | |
| **`Pre-Trained Language Models ( AI 產 )`** | |
| | 方法/子類 | 代表論文/實作 | 核心想法 | 何時使用 | 代價/限制 | 工程備註 | | |
| | --------------------------------- | ---------------------- | --------------------- | ---------- | ----------- | ----------------------- | | |
| | AutoCompressors | Chevalier 2023(基於 RMT) | 將長文遞迴成「摘要向量」做後續段落的軟提示 | 文檔持續閱讀/可快取 | 需訓練;向量可解釋性低 | 對長檔案建立可重用 summary cache | | |
| | LongNET | Ding 2023 | 擴張(dilated)注意力,近線性長序列 | 需要極長上下文 | 需更換架構/權重 | 選用原生長窗模型而非硬擴窗 | | |
| | In-Context Auto-Encoders(ICAE) | Ge 2023 | 可學編碼器把長上下文壓入固定記憶槽 | 需穩定延遲、內存受限 | 需預訓練/指令微調 | 規劃記憶槽數與替換策略 | | |
| | RECOMP(Retrieve-Compress-Prepend) | Xu 2024 | 先對檢索文做抽取/生成式摘要再前置 | RAG 檢索成本過高 | 摘要品質決定上限 | 先抽取再生成;對比學習+蒸餾提升忠實度 | | |
| **`Retrievers ( AI 產 )`** | |
| | 方法/子類 | 代表論文/實作 | 核心想法 | 何時使用 | 代價/限制 | 工程備註 | | |
| | -------------------------- | ----------------------- | ---------------------------------------------- | --------- | ------------- | ------------------------- | | |
| | LLMChainExtractor | LangChain(Chase, 2017–) | 對每份檔用 LLM 抽出與查詢相關的句段 | 要最高相關與可讀性 | 每檔多一次 LLM 成本高 | 先縮小 top-k(4–6)再抽取 | | |
| | EmbeddingsFilter | LangChain | 以嵌入相似度過濾不相關文件 | 高流量、低延遲 | 召回盲區 | 設相似度閾值;與去重搭配 | | |
| | DocumentCompressorPipeline | LangChain | 串接 TextSplitter/RedundantFilter/RelevantFilter | 原文冗長、重複高 | 管線需 A/B 調參 | 典型序列:切塊→去重→相似度→(可選)LLM 抽取 | | |
| 然後這篇文章主要會以 Retrievers 為主,主要的原因在於 Semantic Compression 與 Pre-Trained Language Models 我有點兒想不到怎麼做.學不完啊…… | |
| # 🚀 LangChain 的 Contextual Compression 功能 | |
| 它有提供三種功能,但我們就談前二個,因為第三個就直接將功能合在一起。 | |
| - LLMChainExtractor | |
| - EmbeddingsFilter | |
| - DocumentCompressorPipeline ( 不說 ) | |
| **🤔 LLMChainExtractor** | |
| 首先 LLMChainExtractor 功能白話文就是 : | |
| > 叫 LLM 幫我們來將第一次 retrive 後的結果,再次找出更相關的 doc。 | |
| 範例程式碼如下,其中 4 就是我們這個地方的重點。 | |
| ```ts | |
| const embeddings = new OpenAIEmbeddings({ | |
| model: "text-embedding-3-small" | |
| }); | |
| const vectorStore = await MemoryVectorStore.fromDocuments(docs, embeddings); | |
| const baseRetriever = vectorStore.asRetriever({ k: 10 }); // 先檢索較多文件 | |
| // 3. 建立 LLM(用於抽取) | |
| const llm = new ChatOpenAI({ | |
| model: "gpt-4o-mini", | |
| temperature: 0, // 設為 0 以獲得更確定性的抽取結果 | |
| }); | |
| // 4. 建立 LLMChainExtractor | |
| const compressor = LLMChainExtractor.fromLLM(llm); | |
| // 5. 包裝成 ContextualCompressionRetriever | |
| const retriever = new ContextualCompressionRetriever({ | |
| baseCompressor: compressor, | |
| baseRetriever: baseRetriever, | |
| }); | |
| // 6. 執行查詢 | |
| console.log(`📝 查詢: "${query}"\n`); | |
| const compressedDocs = await retriever.invoke(query); | |
| ``` | |
| 然後這裡有幾個重點要記得 : | |
| > 你第一次 retrieve 有幾個 document,就會呼叫幾次 LLM,你可以用 process.env.LANGCHAIN_VERBOSE = "true" 打開 debug 模式來看看 | |
| 然後我們也順到看看他實際上的 prompt 長什麼樣子,如果之後你自已要實作 LLM compression prompt 也可以參考看看 LangChain 這的 prompt。 | |
| ``` | |
| Query: RAG 如何降低幻覺問題? | |
| Document: "[00:10] 嗯...今天我們要講的是 RAG,就是...那個...檢索增強生成。 | |
| RAG 的核心概念是結合外部知識庫和大型語言模型。 | |
| 它可以有效降低 LLM 的幻覺問題,提供更準確的回答。 | |
| 不過 RAG 也有一些挑戰,比如檢索到的內容可能包含很多無關資訊" | |
| LangChain 產的 prompt ====================================================== | |
| [llm/start] [1:chain:LLMChain > 2:llm:ChatOpenAI] Entering LLM run with input: { | |
| "messages": [ | |
| [ | |
| { | |
| "lc": 1, | |
| "type": "constructor", | |
| "id": [ | |
| "langchain_core", | |
| "messages", | |
| "HumanMessage" | |
| ], | |
| "kwargs": { | |
| "content": "Given the following question and context, extract any part of the context *AS IS* that is relevant to answer the question. If none of the context is relevant return NO_OUTPUT.\n\nRemember, *DO NOT* edit the extracted parts of the context.\n\n> Question: RAG 如何降低幻覺問題?\n> Context:\n>>>\n\n[00:10] 嗯...今天我們要講的是 RAG,就是...那個...檢索增強生成。\nRAG 的核心概念是結合外部知識庫和大型語言模型。\n它可以有效降低 LLM 的幻覺問題,提供更準確的回答。\n不過 RAG 也有一些挑戰,比如檢索到的內容可能包含很多無關資訊。\n\n>>>\nExtracted relevant parts:", | |
| "additional_kwargs": {}, | |
| "response_metadata": {} | |
| } | |
| } | |
| ] | |
| ] | |
| } | |
| ``` | |
| **🤔 EmbeddingsFilter** | |
| > 事實上它就只是 retrive 後根據它的 score 進行 filter。 | |
| https://js.langchain.com/docs/how_to/contextual_compression/ | |
| LangChain 中有個叫 ContextualCompressionRetriever 的東西,可以將我們第一次 retrive 後的東西,再進行 compressing,其中 EmbeddingsFilter 就是的地方。 | |
| ```ts | |
| const docs: Document[] = […… 你的原始資料]; | |
| const query = "如何在 RAG 降低成本與去除無關內容?"; | |
| // 2) 建 vector store + 基礎檢索器 | |
| const embeddings = new OpenAIEmbeddings({ model: "text-embedding-3-small" }); | |
| const store = await MemoryVectorStore.fromDocuments(docs, embeddings); | |
| const baseRetriever = store.asRetriever(12); // 先取寬一些 | |
| // 3) EmbeddingsFilter:設定門檻與最多保留數 | |
| const compressor = new EmbeddingsFilter({ | |
| embeddings, | |
| similarityThreshold: 0.5, // 0~1,語料越同質可拉高 | |
| k: 4, | |
| }); | |
| // 4) 包裝成 ContextualCompressionRetriever | |
| const retriever = new ContextualCompressionRetriever({ | |
| baseRetriever, | |
| baseCompressor: compressor, | |
| }); | |
| // 5) 查詢 + 輸出 | |
| const reduced = await retriever.invoke(query); | |
| ``` | |
| 然後我當初在看這東西時覺得很出怪。 | |
| **因為它不就是一個根據第一次 retrive 後的分數,來再根據 similarityThreshold 進行一次塞選嗎 ?** | |
| 我們是不是也可以用這種寫法來處理呢 ? | |
| ```ts | |
| // ✅ 技術上完全可行 | |
| const resultsWithScore = await store.similaritySearchWithScore(query, 12); | |
| const filtered = resultsWithScore | |
| .filter(([doc, score]) => score >= 0.5) // 手動過濾 | |
| .slice(0, 4) | |
| .map(([doc, score]) => doc); | |
| console.log(filtered); | |
| ``` | |
| 原理上是對的,而且我以為他是有在 embedding 過,但發現沒有。 | |
| 那為什麼 LangChain 還要提到這個呢 ? 因為以下幾個原因 : | |
| - 不同的 VectorStore 分數計算方式可能不一致。 | |
| - 某些 VectorStore 不支援 withScore。 | |
| 所以事實上還是會建議使用。不過有點奇怪 1.0.0 的文件沒看到這個章節,只有在這裡有看到,不確定他們是不是偷偷讓每個 Store 的分數都統一了…… | |
| https://v02.api.js.langchain.com/classes/langchain.retrievers_contextual_compression.ContextualCompressionRetriever.html | |
| # 🚀 實作 - 整合到字幕檔實作 AI 課程問答功能 | |
| 接下來我們將上面的東西,整合到我們的功能中。 | |
| 這個地方我們就只實作 EmbeddingsFilter,主要的原因在於 LLMChainExtractor 真的有點太耗錢了,所以除非結果真的非常不理想,不然應該還是先考慮只用 EmbeddingsFilter。 | |
| 然後接下來我們來看程式碼修改後的地方。 | |
| 首先最外層還是一樣沒變,如下,然後改變的是在 Stage 2 的 Vector Search 中,會加入相關的功能。 | |
| ```ts | |
| const query = async (message: string) => { | |
| // ===== Stage 1: Query Expansion ( Pre-Retrieval ) ===== | |
| const queryVariants = await this.generateQueryVariants( | |
| originalQuery, | |
| this.config.numQueryVariants | |
| ); | |
| const hypotheticalAnswer = await this.generateHypotheticalAnswer( | |
| originalQuery | |
| ); | |
| const searchQueries = [originalQuery, ...queryVariants, hypotheticalAnswer]; | |
| // ===== Stage 2: Vector Search ===== | |
| console.log(`\n--- Stage 2: Vector Search ---`); | |
| const candidates = await this.vectorSearch( | |
| searchQueries, | |
| k * this.config.retrievalMultiplier | |
| ); | |
| // ===== Stage 3: Temporal Cluster ( Post-Retrieval ) ===== | |
| const clustered = this.temporalReranker.rerank(candidates, k * 2); | |
| // ===== Stage 4: Voyage Reranking ( Post-Retrieval ) ===== | |
| const contexts = await this.voyageReranker.rerank(originalQuery, clustered, k); | |
| // ===== Stage 5: 將 Context 代到 Prompt 中生成答案 ===== | |
| const result = await model.invoke([ | |
| { | |
| role: "system", | |
| content: ` | |
| # Context: ${contexts | |
| .map((c, i) => { | |
| return `[${i + 1}] 時間: ${formatTime( | |
| c.metadata.start_ms | |
| )}-${formatTime(c.metadata.end_ms)} | 相關性: ${ | |
| c.rerank_score?.toFixed(3) || "N/A" | |
| } | |
| 內容: ${c.pageContent}`; | |
| }) | |
| .join("\n\n")} | |
| # Instructions: | |
| - 你只能根據 Context 回答相關的問題 | |
| - 說明答案的來源時間範圍(格式: "MM:SS~MM:SS") | |
| - 限制在 500 個字以內 | |
| - 如果 Context 中沒有相關信息,誠實告知 | |
| `, | |
| }, | |
| { role: "user", content: message }, | |
| ]); | |
| }; | |
| ``` | |
| 下面程式碼就是 vector search 裡面,然後我們有加上了 EmbeddingsFilter ,然後透過 ContextualCompressionRetriever 將會根據 similarityThreshold 來進行 compress。 | |
| 但是這裡我實驗後發現,如果我將 similarityThreshold 設為 0.7 後,就幾乎都拿不到結果,但他的確幫我們移除掉了很多不相關的資料,因此在後面的處理就更省空間與速度了,的確幫助很大。 | |
| ``` | |
| const baseRetriever = await this.vectorStore.asRetriever( | |
| Math.ceil(totalK / queries.length) + 5 | |
| ); | |
| // ===== Step New: 加上 Contextual Compression Retriever ===== | |
| const compressor = new EmbeddingsFilter({ | |
| embeddings: this.vectorStore.embeddings, | |
| similarityThreshold: 0.5, // 0~1,語料越同質可拉高 | |
| k: 4, | |
| }); | |
| const retriever = new ContextualCompressionRetriever({ | |
| baseRetriever, | |
| baseCompressor: compressor, | |
| }); | |
| ``` | |
| 事實上沒啥技術,但也是種思路。 | |
| # 🚀 小總結 | |
| 今天的文章我們大概看了一下整個 Context Compressing 的方法體系,看完後真的發覺得水好深,所以我們最後只抓了 Retrievers 那個地方的手法來實作,事實上我自已覺得效果算不錯,已經清掉不少不需要的 context 了,但就只是覺得好像沒啥技術成分在。 | |
| 這篇我自已覺得有點水誒 Semantic Compression 的手法都沒實作到,唉 ~ | |
| # 🚀 參考資料 | |
| - [langChain-contextual_compression](https://js.langchain.com/docs/how_to/contextual_compression/) | |
| - [Contextual Compression in Retrieval-Augmented Generation for Large Language Models: A Survey](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2409.13385) |
Sign up for free
to join this conversation on GitHub.
Already have an account?
Sign in to comment