- PHP/java
- Method are part of class.
package unl.cse // package declaration
//import library would go here.
/**
* A basic hello world program in java
*/
public class HelloWorld{
public static void main(String args[]){
System.out.println("Hello World!");
}
}- package
- allow you to organize code into an tree-like structure.
- period delimit packages-subpackages
- naming convention: all lower case.
- class.
- in java, Everything in a class belong to a class
- Naming convention:
UpperCaseCamel
- Main method declaration
- Every program that need to be
runshould have amainmethod - main is the identifier/ name for the method.
- public: access specifier.
static keyword: remain constant.voiddoes not return anything
- Every program that need to be
- standard I/O
System.out.println("CONTENT_HERE");
- command line
- Compile :
javac helloWorld.java// javac: compiler, java: interpreter. - produce a
.classfile(java ByteCode) - Run :
java helloWorld - check out this link on how to compile java with multiple class
- or how to compile java with additional library.
- https://stackoverflow.com/questions/18093928/what-does-could-not-find-or-load-main-class-mean?utm_medium=organic&utm_source=google_rich_qa&utm_campaign=google_rich_qa
- Compile :
- IDE(Eclipse)
- Create a project, package, class,
- Compiling: automactic, running.
- refer to lab01. on how to compile with addtional library
.jarfile.
- develop an online social network like facebook, instagram, or a blog
- specified by the
data type - have 2 type of data type
- Primitive: int, double, float, char, byte, ..
- Reference: String , classes, array(is a class)
- Pimitive type is
built in- byte,short, int, long, float, double, boolean, char.
- Computer treat character as a number
- jave represent character by
unicodeUnicodeinclude ASCII code
- Java is STRONGLY TYPED and STATICLLY TYPE
- naming convention:
lowerCaseCamelCase(thisIsAnExample) Scoping rulevariable are only validwithin the blockin which they are declared
//java allows implicit upcasting
int x = 10; // ocupies 4 byte
double y = x; // ocupies 8 byte
// java does not allow implicit down-cast
// this code is an complication error
double x = 10.5
int y = x;
//explicit type casting is reuired
double x = 10.5;
int y = (int) x;- primitive data type is
not Object - Some time we need to cnvert datatype into
object- why? so we can use it like reference like c.
ArrayList<Integer>Integer is an object- ArrayList is difference than array. ArrayList can store wrapper classes
- nutShell: pimitive type-> object contain promitive type.
- You cannot change it after declare as wrapper class
int i = 100;
// you can store anything in a box ???
// array list, array , anything?
//wrapping
Integer ib = new Integer();
// unwrapping
int iu = ib.intValue();- primitive and reference type
does notstore in a same fashion - primitive store content.
- reference store memory
- array
- conditional
- array, conditional, type juggling
int anArray[] = {45,1,2};
int position1 = anArray[0]; // base 0
int lengthOfArray = anArray.length();// return the length of the array
//Declare static array
int intArray[] = new int[3];// create int array to store 3 elements
// later assign value to it.
//multi dimensional array
int matrix[][] = new int[2][3]; // create a 2x3 matrix.
int position11 = anIntMatrix[0][0];- key limitation of array.Problem: fixed size;
- Dynamic collection alternative :
ArrayList
//delcare an Integer ArrayList(dynamic)
import java.util.ArrayList;
ArrayList<Integer> anIntArrayList = new ArrayList<Integer>();
// use the "add" method to store elements.
anIntArrayList.add(34);
anIntArrayList.add(12);
anIntArrayList.add(23);
System.out.println("3rd array element"+anIntArrayList.get(2));// get 23- some application you need to use
key-value pair- EX: NUID && student. Account & routing number
- We need to use
Map Interface - hashMap (hash table)
- require alot of memory
- Hashmap does bot guarantee order
- if you want maximum speed and don't care about order, then use hash map.
import java.util.HashMap;// does not store in order
import java.util.Map;
Map<Character,Integer> firstTenLetter = new HashMap<Character,Integer>();
int i = 0;
for(char letter = 'a'; letter <= 'j'; letter++){
firstTenLetter.put(letter,i);
i++;
}
System.out.println(firstTenLetter);
//{f=5,g=6,e=4,b=1,c=2,a=0,j=9,h=7,i=8}- treeMap
- if you need sorted map
- it implementation is based on the
red-black treedata structure.
- LinkedHashMap
- if you want
near-hashMap performanceandinsertion sortiteration, use LinkedHashMap. - it implement base on
hash tableandlinked list
- if you want
- same as c
- switch
- switch only check 1 value.
char grade = 'A';
switch(grade){
case 'A':
System.out.println("apple");
break;
case 'B':
System.out.println("banana");
break;
}switchdoes not support float and double. only small storage primitive tyepfloatanddoubleis too bigstringsupportswitchstatement.switchsupportbyte,short,int,char or String
- 3 basic loop :
for,while, anddo-while( same syntax as C) - to print array use for loop/
forloop need to determine how many elements are in the array . There for we useEnhanced for-loop.
int [] squares = {2,123,12,12,34,5};
// to print out all elements
for(int i = 0;i < squares.length; i++){
System.out.println(i);
}
// another faster
// Enhanced for loop
// don't need to know the size of the array
// print all in th\e array
for(int i : squares){
System.out.println(i);
}
//enhance for string
String [] names = {"Mozart", "Jess", "Potter"};
for(String name: names){
System.out.print(name);
System.out.print(",");
}
// use enhanced loop fr mapping
map<Character, Integer> map = ....;
for(char x: map.keyset()){
....(map.get(x));
}Stringin java is aclass.- sometime, we need to
concatenate(add)String. Be becareful, or you will end up with an inefficient solution. - Concatenation operator :
+; - Concatenation method:
concat()
String string1 = "UNL";
String string2 = "is a beautifl place";
// theses below will do same thing
string1 = string1 + string2;
System.out.println(string1);// print "UNL is a beautiful place"
string1 = string1.concat(string2);
System.out.println(string1);- Strings are
immutable- obj whose statecannot be changedafter construction - If you set it equal to something else incorrectly. the 1st String will lost reference.
String string1 = "UNL";
// this line will cost "UNL" to lost Reference
// point string1 to "UNL is beautiful" but "UNL" is still in memory.
string1 = "UNL is beautiful";
String string1 = "life";
string1.concat("is beautful");// string1 still point to "life"
// this would cause string1 to point to differe"nce direction
string1 = string1 + "is Beautiful";
// string1 point to "is Beautiful now."-
You waste a lot of space.
-
SOLUTION:create multable stringStringBuilders
StringBuilder string3 = new StringBuilder("Life");
string3.append("is Beautiful");// or concatenate
System.out.println(string3);// >> "Life is beautiful"
// logic: make bigger space for string3 when add something . instead of point it to somewhere else.StringBuilderis faster but as it isnot thread safe.- use
StringBuffer
- use
- e cannot compare te content of 2 reference type object.
// this would cause FALSE
String string1 = "Hello";
String string2 = "Hello";
// string1 and string2 point to difference spot of memory. there
// for, this wouldcase false.
if(string1 == string2){
System.out.println("TRUE");
}else{
System.out.println("FALSE");
}
//>> SOLUTION
if(string1.equals(string2)){
System.out.println("TRUE");
}else{
System.out.println("FALSE");
}- use
==for ptimitive type only. - use
.compareTo()to compare string- work same as
strcmpin C
- work same as
-
An exception is a problem that arise during the execution programm.
-
exception may lead to
terminationof the programif not handled properlt -
Execption can occur for may difference reason;
- User jas entered
invaliddata - A
filethat needs to be openedcannot be found
- User jas entered
-
goal to
maintain the flowof a program even if exception arise during its excution -
Uncought exception may kill the
JVMprocess. -
throwableis the parent class of all exceptions.-
extend:
Exception- Unchecked/Runtime excepions ( ArithmeticException, nullPointerException, ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException) _
- Checked excetion(IOException, SQLExcetion)
-
Error -
checked exception, in the example below
javadoes not know if the file exist or not yet, so we need to tell what it will do .- adding
throwright at the at the function will return runtime exception
- adding
-
//
Scanner scan = new Scanner(new File("data/file.txt"));
// by adding try/catch block it will printout the error and continue excute the code below the block
Scanner scan = null;
try{
scan = new Scanner(new File("data/file.txt"));
}catch(FileNotFoundException e){
System.out.println("FILE not found");
}
System.out.println("This line still run");- The idea of OOP is to reuseable
- like a car. a car got asseamble from multiple component. same with software, you can assemble software component.
- OOP language premit
higher level of abstractionto solve real life problem. - well encapsulated objects
interactwith each other bysending message - benefit:
- ease of software design(think more like human)
- maintainance
- reuseable
- Absatrction
- is the process of
hiding the implmentation detailand exposing only the essential freature. - focusses on an outside feature. like driving a car. don't let user car about how car work.
-
- involves 4 min principles:
- Abstraction
- Encapsulation
- Inheritance
- Polymorphism
- is the process of
-
2 obj can respond to the
same messagein different ways. - according to their nature.- ex: same car. but different type of car.(honda, ford, tesla)/
-
Java is not a pure OOP language, but pretty close. primitive type are not objects.
- some method come from object Superclass
clone(): Creates and returns a copy of this object- equals(Object obj): Indicates whether some other object is “equal to” this one
finalize(): Called by the garbage collector on an object when garbage collection determines that there are no more references to the objectgetClass(): Returns the runtime class of an objecthashCode(): Returns a hash code value for the objecttoString(): Returns a string representation of the objectequals()returns true/false whether or not obj is equal to this- Default behavior: uses reference comparison
hashCode()returns an integer hash of this object- Default behavior: typically the memory address of the object
toString()provides a human readable representation of the object- Default behavior: qualified class name plus JVM memory address
Abstractionis the mechanism by which objects are given their representation- Ex:
qsort()in C, how does it swap?, tempory space?- who cares??
sqrt()function may be implment using Taylor series, balbylonia method. who cares?
-
Grouping of data
-
Protection of data
-
Grouping of methods that act on an object's data
-
f))orm of information hiding -
refer to Car example project for more detail about abstract classes and inheritance example
/*Shallow copy*/
// say initializa an object
Car c = new Car("White"); // you usually use keyword "new" to create new memory space ;
// init c with "white" color
// c2 would point to the same address that c have.
Car c2 = c; // this is a shallow copy
c2.setColor("red");// this will make c and c2 become "red"
/*Deep Copy */
/*Way to solve this problem */
Car c = new Car("White"); // you usually use keyword "new" to create new memory space ;
Car c2 = new Car(c);
c2.setColor("Red");
// now c = "White";
// c2 = "red";- Inheritance
- Def: Creating object from previously created or defined objects.
- Human are good at patern recognizing.
public class Bird{
public move(){
System.out.println("Move! Somehow");
}
}
public class Robin extends Bird{
}
public static void main(String [] args{
Bird b = new Bird();
Robin r = new Robin();
Ostrid o = new Ostrid();
b.move();
r.move();
o.move();
}
>>OUTPUT
> Move! Somehow
> Move! Somehow
> Move! Somehow-
java does
not supportmultiple inheritance. c++ does.- java does not support mult inheritance. like DogCat Object PosNeg Class.
-
class Composition
- book :
the woman who changed her brain
- Method overloading in java.
public void function(arg1 , arg2, arg3){}
public void function(arg1,arg2){}-
the above function have same function but 1 takes 2args and 1 take 3 arg.
-
Opperator overloading
String+Stringmay beconcatenation- number + number may be
addition
-
Overriding : Same method, same name, same number of argument.
- The ability to replace inherited method in the subclass.
finalavoid Overriding by the children.@Overrideannotation is an annotation to tell compiler that you are overridiing something. you don't relly need it. Just something to double check.
-
Object Casting
- Robin -> Bird (Covariant)
- Bird -> Ostrid(Contravariant)
- Robin -> Ostrid(Invariant)
-
Autoboxing
- A collection contains only
Obect - if you want a collection of
primitive typeyou need to box it.
- A collection contains only
Integer anInteger = 10;// autobox from int to integer
int i = anInteger; // auto unboxing.- Universal Polymorphism is the ability to handle type universally.
Inclusion Polymorphism- replacing the super type's instance with a subtype's instance.
public static void main(String args[]){
Bird aRobinbird = new Robin();
Bird anOstrichBird = new Ostrid();
}- to make function generic place Object parameter with
Objectparamter
public void print(Object obj){
System.out.println(obj);
}- upcast is
saferthan downcast- ex: int -> double - this is more safe than double -> int
- ex: cast from child to parent is safer than parent to children
- you don't lose info by upcast.
- Integer cannot be easuly cast to String . ( Classexceptionerror)
- Use
instanceofwhen down cast.
for(Product p: list){
if(p instanceof MovieTicket){// check if we can cast it.
// cast to ovie ticket if obect is
MovieTicket m = (MovieTicket)p;
}
}parametric Polymorphism- make function generic to make life easier
- EX:
//List ont the left and ArrayList on the right// inclusion Polymorphism
List<Integer> intList = new ArrayList<Integer>();
List<String> stList = new ArrayList<String>();
List<Object> objList = new ArrayList<Object>();- generic
printList()function
public static <T> void printList(List<T> aList){// choose Any letter . prefer "T"
for(T anElement: aList){
System.out.println(anElement);
}
}
printList(intList);
printList(stList);
printLIst(objList);- multiple parameter types: <T,U>
- example of generic class
public class ContainerGeneric<T>{
private T t;
public T get(){
return t;
}
public void set(T t){
this.t = t;
}
}// end class ContainerGeneric
public static void main(String[] args){
ContainerGeneric<String> a2 = new ContainerGeneric<String>();
a2.set("Alan Turing");
Integer s2 = a2.get(); // this would cause a compile-time exception
// you set a2 to be String but you are trying to store Integer.
}- Naming convention for
genericin java
E – Element (used extensively by the Java Collections
Framework, for example ArrayList, Set etc.)
K – Key (Used in Map)
N – Number
T – Type
V – Value (Used in Map)
S,U,V etc. – 2nd, 3rd, 4th types- use
<? extends type>for class - and subclass(String) - un interesting java hack
type eraser
List <Integer> intList = new ArrayList<Integer>();
// when compiler compile it ignore the type
// this only happen at the compiler time. you still need to write the type though
List intList = new ArrayList();- Problem
- create a diffrent types of geometrical shapes and compute their area.
- ex: circle, oval,
- Shape class , define
getArea()as an abstract class( a method signature) - Advantage: you dont define actual
getArea()until you define the actual shape classes.
abstract public class Shape{
public abstract double getArea();
}-
Interface and Implementsee lecture 16. -
Shoe Example.
public class Shoe implement Comparable {
private boolean hasShoeLace;
private int size ;
private String material;
private String brandName;
private String type;
// constructor
public Shoe(int size, String material, String brandName, String type){
if(type.equals("closed")){
this.type = type;
this.hasShoeLace = true;
}else{
this.type = "open";
this.hasShoeLace = false;
}
this.material = material;
this.brandName = brandName;
this.size = size;
}
// Auto generate getter- setter.
@Override
public compareTo(Object o){
// sort by brandName
if(o instanceof Shoe){
Shoe s = (Shoe)o;
return this.brandName.compareTo(s.getBrandName());
//return (new Integer(this.size)).compareTo((new Integer(s.getSize()));
}else{
return 0;// only compare shoe.
}
}
@Override
public String toString(){
return this.brandName +"; "+ this.size;
}
}
publiic class Driver{
public static void main(String args[]){
Shoe s = new Shoe(11,"concrete","ModHitShoe","Closed");
Shoe s2 = new Shoe(10,"Plastic","Nike","closed");
Shoe s3 = new Shoe(1,"Wood","Cloas","open");
ArrayList<Shoe> shoes = new ArrayList<Shoe>;
shoes.add(s);
shoes.add(s2);
shoes.add(s3);
}
for(Shoe next: shoes){
System.out.println(next);// print out what ever in the toStrind method.
}
Collections.Sort(shoes);
for(Shoe next: shoes){
System.out.println(next);// print out what ever in the toStrind method.
}
}- imagine when write a program it does not live forever. when you stop all data lose.
- One way to get around is to store data in database.
- inefficient if store in flat data and read it
everytimeyou run the file . - every group running the program need to execute the file. again . this is
redundance - Piece of data is store at difference place and difference gruop. for ex, GPA and student fee is store at difference location or by diff gruop.
Databasesis a single repository define data in one placeto reque
- you need to send a
queryto request data.
- in the past, use flat model, hierachy, relational model, Object-oriented model. Network model.
- we use
Relational model Relational modelis base onset theoriesandfirst predicated order- Relational model is basicly excel- or store data in a table( have unique name and type description).
Attribute- col;tuple- row
- MYSQL Cheatsheet
- via cml
mysql -p
- Via workbench
- MySQL WorkBench provide by oracle
mysql -u username -p database_name < file.sql // load database
USE dbname;
SHOW TABLES;
DESCRIBE tablename;
- student alow 1 DataBases
- You cannot make new database.
user USER_NAMEto show databases under your user name
-
note: sql cmd are not case sensitive/.
-
Create table
CREATE table_name (
column_name1 data_type(size),
column_name2 data_type(size),
column_name3 data_type(size),
...
);
VARCHAR(n)variable length character field ( max 255)INTEGER or INTFLOAT
CREATE TABLE Customer(
id INT NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,// increase id every new row mySql create.
name VARCHAR(255),
ssn INT DEFAULT'-999',
address VARCHAR(255)// if you want adddress to reference another table
// this would hold and int foriend key ref other table.p
//UNIQUE(id)
//or
//PRIMARY KEY(id,ssn) // more than one primary ey
//PRIMARY key: is what ditinquish the row.
);
- A
primary keyallows us to give each record aunique identity - You can have at Most on primary key per table
NOT NULLUNIQUEPRIMARY KEY- A primary key column often has AUTO_INCREMENT attribute that generates a unique sequence for the key automatically.
FORIENGN KEYCHECK- check that all col conditionDEFAULT
CREATE TABLE Customer (
id INT AUTO_INCREMENT, // default not need to set
name VARCHAR(255),
ssn INT DEFAULT ‘-999’,
address VARCHAR(255),
PRIMARY KEY(id)
);
ALTER TABLE [table_name] ADD COLUMN [column_id_name] INT NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT KEY;
INSERT INTO Customer(id,name,ssn,address) VALUES (123,'FeyMAN','733','California')- when inserting you dont need to insert ID since ID is auto increment.
INSERT INTO Customer(id,name,ssn,address) VALUES (123,'FeyMAN','733','California')
- use
LAST_INSERT_ID()function the get the most recent added AUTO_INCREMENT value in a table
- Syntax:
SELECT column1,col2.. FROM TABLE WHERE (condition)
- EX:
-select all colun using wildcat.
- sql allow us to alias a name - "rename"
SELECT name AS Cus_Name FROM Customer;
- exist data can be change using the
UPDATEstatement - Should be use in conjunction with clauses ( where, ..)
- Syntax:
UPDATE table_name SET col1 = value1,//more.
DELETE FROM Customer WHERE id = 123;
- the
LIKEclause used in conjunction with the wildcard- ex: find a book year that start with 20
INclause- basicly
IN=isequals()cmd in java
- basicly
- Nested query with
INclause- SELECT * FROM Book WHERE isbn IN(SELECT isbn FROM Library WHERE num_copies > 50);
ORDERClause- ex:
SELECT * FROM Book ORDER BY title;// automaticly increase - // define // DESC to order in desc
- ex:
ALTER TABLE table_name ADD PRIMARY KEY (column_name);ALTER TABLE table_name DROP PRIMARY KEY;
- Table with foreign key(referencing) reference table with primary key(referenced table)
- Syntax:
FOREIGN KEY(column) REFERENCE table(column)
- EX:
CREATE TABLE Product (
p_id INT,
description VARCHAR(255),
cust_id INT,
PRIMARY KEY(p_id),
FOREIGN KEY(cust_id) REFERENCES
Customer(id)
);
- The
LIKEclause is used in conjunction with the stringwildcard % - EX:
- sorting the record in ascending order by default
- Usually use at the end of a query
- ex:
SELECT * FROM book ORDER BY title;sort by ascendingSELECT * FROM book ORDER BY author DESC, title ASC;
//- year starting with 20
SELECT * FROM Book WHERE year LIKE ‘20%’;
//- Year ending with 00
SELECT * FROM Book WHERE year LIKE ‘%00’;
//- author contains the pattern Escher
SELECT * FROM Book WHERE title LIKE ‘%Escher%’;- first grant access run after run
mysql -u root -pGRANT SELECT ON *.* TO 'username'@'localhost';CREATE DATABASE dbname;// create database nameUSE dbname;// use DataBasesshow databases
- to add a database table downloaded to your folder.
- navigate to the database with the
.sqlfile - run
sudo mysql -u root -p mysql < Albums.sql
- navigate to the database with the
- On your system, exist (one database) use
use mysql;cmd to use my sql database.
- Run
drop database db_name;
- How do we get a count of the nmber of row?
- How do we get max/min value?
- How do we get the average value
- How do we compute the total of a total copies of a specific author?
- we can write java code to process data and compute
Not efficient
- More efficient solution: use databaases aggregation functions.
- allow us to compute adata on the DataBases with out processing all the data.
-
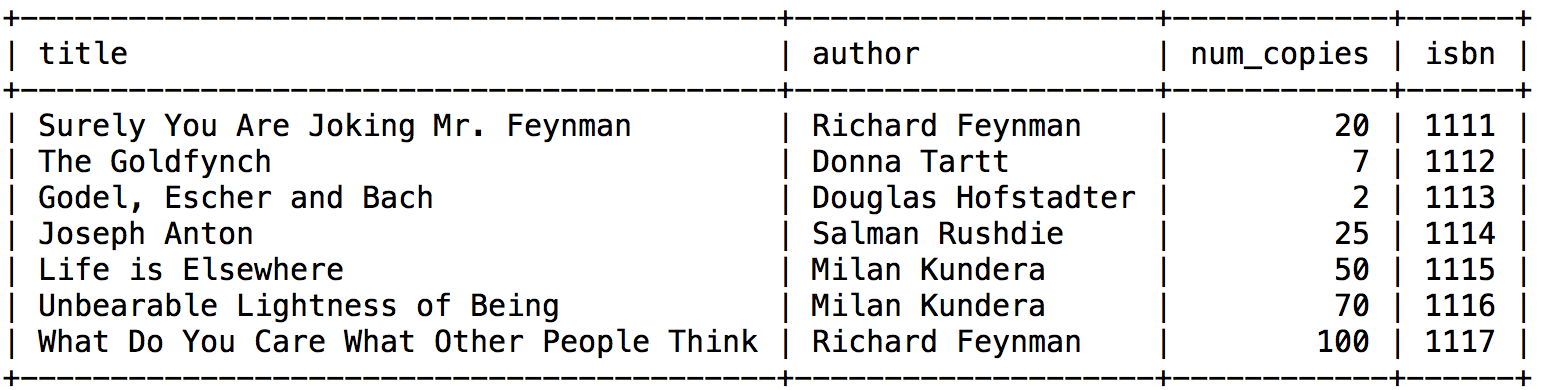
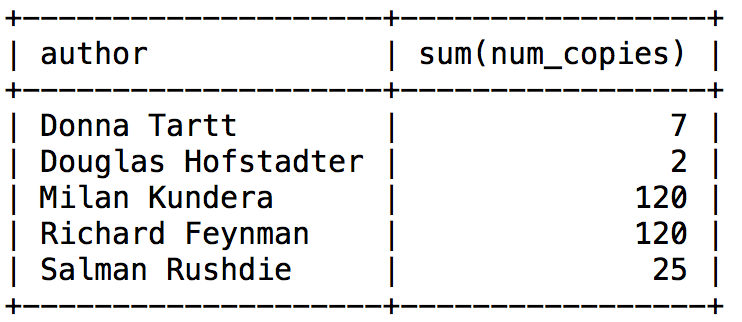
COUNT()- Returns the number of rowsselect COUNT(*) AS Num_Of_Records FROM Book;// return the count of the number of book recordSELECT author, COUNT(author) as Num_of_Titles from Library WHERE author = 'Richard Feynman';//return 2 col. one author and one numOfinstance taht author appear on the database table
-
SUM()- Returns the sumSELECT author, SUM(num_copies) as TOTAL_COPIES from Library WHERE author = 'Richard Feynman';# total of all copy- For using SUM on
non-numericcol SUM function will return 0;
-
MAX()- Returns the largest valueSELECT MAX(num_copies) FROM Library;
-
MIN()- Returns the smallest value -
AVG()- Returns the average value -
FIRST()- Returns the first value -
LAST()- Returns the last value -
How do we get the book that were publish during max year from Book table?
SELECT * FROM Book WHERE year = (SELECT MAX(year) FROM Book);
- Find the group of rows for the same author and compute the sum of copies.
select author, sum(num_copies) from library group by author;- You can use with the ORDER BY in conjunction t
- enable us to specify condition that filter which
group resultsappear in the final result.SELECT author,sum(num_copies) from Library GROUP BY author HAVING sum(num_copies)>10;
- A clause that combine records from 2 or more tables.
- Type:
- (INNER) JOIN
- LEFT (OUTER) JOIN
- RIGHT (OUTER) JOIN
- FULL (OUTER) JOIN
- Other join:
- Self-join
- cross join(catesian product)
- everything on left( first) table will be reported. part of table 2(where there is matching data) will be reported.
SELECT column_name(s) FROM table1 LEFT JOIN table2 ON table1.column_name=table2.column_name;
-
mysql does not support FULL JOIN
-
we have to use
union all- refer to page 39-42 for syntax.( Lecture note 20 -MYSQL-2)
-
more example:
- may want to query only the unqiue value(ex: number
DISTINCTauthor)SELECT DISTINCT author FROM Library;
- may want to count up the nunber of unique values
select COUNT(DISTINCT author) FROM Library
- Identify all
entitiestoo store them differently. - Foreign key.
- should be integers( not var, nor float)
- SHould not be based on external identifiers that
are not controlled by the databases( NUID,..)
- One to one
- Husband <-> Wife
- Problem/solution: if the relationship is
one to onethen just combine them as one table why split them into 2 table.husband/wifewill be store in the same table.
- Problem/solution: if the relationship is
- Husband <-> Wife
- One to many
- Author -> book1 / book2 ( one author can write mult books)
- Many to one
- bool1/book2 -> Author
- Many to many
- need a join table
- How many table should we have ?
- How large/small should be a table?
-
Normalization is structly organiza data.
-
refer to the 3rd level
-
1st Normalization
- Eliminate duplicate column from the same table
- store same data in databases tabl else {
- should not have a repeted col with new info.
-
2nd Normalization
- apply foreign key
- meet all requirement in 1st Normalization
- don't duplicate data but split them.
- for ex: address you need Address table, zip table, state table, city table. to prevent duplicate
- Do this if you want efficiency
-
3rd level of relation
- mean free of insertion, update, and deleteio
anomolie
- mean free of insertion, update, and deleteio
-
When do we need to override them.
-
why?
- If 2 obj are equal according to their equal method) then they must have the same hashcode.
- If two object have the same hash code, they may or may not be equal
- Because java split value and key to difference bucket(or multiple list holding hashcode) refer to lecture note p34 for more info
-
In java, when comparing object, Even though they have the same attribute, but the
.equals()method will result afalsemeaning not equal because they have difference hash value. -
equals()method compare the hash value as well as attribute to determine if 2 obj are equal -
When create new object, same object might have different hashcode value. because the same object might spread out among different hash bucket.
-
We need to
overridethe hashcode functiongoal:is to give the same memory address for the equal object.
-
The easiest way to
override hashcode and equalin java(eclipse IDE),- Source à Generate hashCode() and equals()
-
provide a standard library for accessing relational databases
-
You can access most relational databases
-
Not an acronym(really not) java database connectivity -
API: application program interface. -
Tool to:
- Making connection to DB
- create SQL statement
- viewing and modifying
-
install appropriate JDBC driver -
import java.sql.* -
Register JDBC Driver
- Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver")
-
Open Connection
-
execute query
-
Extract data from result
while(rs.next()){......}- use
getto get token in row.getStringgetInt..... - ResultSet rs is not a string.
while(rs.next()){
int id = rs.getInt("ID");// ID is the col name
String first = rs.getString("First_Name");// First__name is the col name
String last = rs.getString("Last_Name");
}-
Clean up the environment
rs.close();stmt.close();conn.close();
-
Create and close
- use
trycatchandfinallystatement to open and close connection
- use
-
create jdbc as a classe
- first make a new project
-
prepared statement
?is a place holder in a query- use
ps.setString(1,lastName);ps: PreparedStatement - in this way you prevent not to set error at run time.
- ALWAYS use
PreparedStament
- because it prevent
SQL injection - if don't use
PSthe attacker will trick the interpreter toexecute uninted command - For example:
String query = "SELECT * FROM PRORUCT WHERE"+ lastNamewherelastNameis a variable You can fill inlastNamewithDROP tablethis would be uninted query that attacker input. UsingsetString(), setInt()you promt the user foronlyastringorint
- Get only infomation you want when using
SELECTclause - Refer to the note to know how to make password encrypted.
- Problem with array
- Once created, capacity is fixed
- cannt dynamiclly change
Better SolutionUsing a list
- Def: A model to create a data structure.
- First declare the core function
- Adding element
- Retrieve elements
- Removing element
- Automatic resize
-
Demo Building Int Array list
- Look at
ADT lecture notefor more detail - IDEA: Resize and shifting when create and adding element.
Using Array base list is
Not a good solutionNot Generic
- Look at
-
Instead we shoudl generalize it to take any element( Obj and any type)
-
Linked list
- value
- Pointer to the next node,
-
Need to handle corner cases
-
Creating a linked list
- Create the node
- A Class : contain value and the next node.
- Create linked list class
- A class: start and end node and size as attribute.
compareTo(object)
public class Student implments Comparable<Student>{
//method go here
//constructor
@Override
public int compareTo(Student st){
return this.nuid.compareTo(st.getNuid());
// or y9ou can use if else to do it.
// if 2 nuid is equal
// muilti level with comparable interface.
int comp = this.nuid.compareTo(st.getNuid());
if(comp == 0){
comp = this.____.compareTo(st.get___());
}
return comp;
}
//use it in generic way
public int compareTo(Object o){
}
}-
Comparator provide multiple way of sorting object.
public int compare(T o1, T o2); Comparator<Student> byName = new Comparator(){ public int compare(Student st1, Student st2){ int comp = st1.getLastName().compareTo(st2.getLastName()); if(comp == 0){ comp = // compare more attribute here } return comp; } };
- To Write it in one line, one place. Comparator can only be use once.
- To prevent
code reuse adhocksorting - sorting on the fly.
Collections.sort(al,new Comparator<Student>(){
@Override
public int compare(Student st1, Student st2){
return (st1.getNuid() - st2.getNuid());
}
}) ;- sort it when you add in.
head recursion= perform the recursion call first( inefficient)tail recursion= perform cursioncall last- more efficient, does not cause stack to overflow
One way to prevent bad recursion, we can use
memoizationlook at lecture note forcsce155efor more infobasicly store the result that you ahve compute to memory can retrieve, you don't have to recalculate it again;
public static int tailRecursion(){}-
Algoritm an precise recipe with sequence of step.
-
RUnning time of a computer depend on:
- Processor(singlle/unit)
- Read/write speed to memory
- 32 vs 64 bit
- input size
-
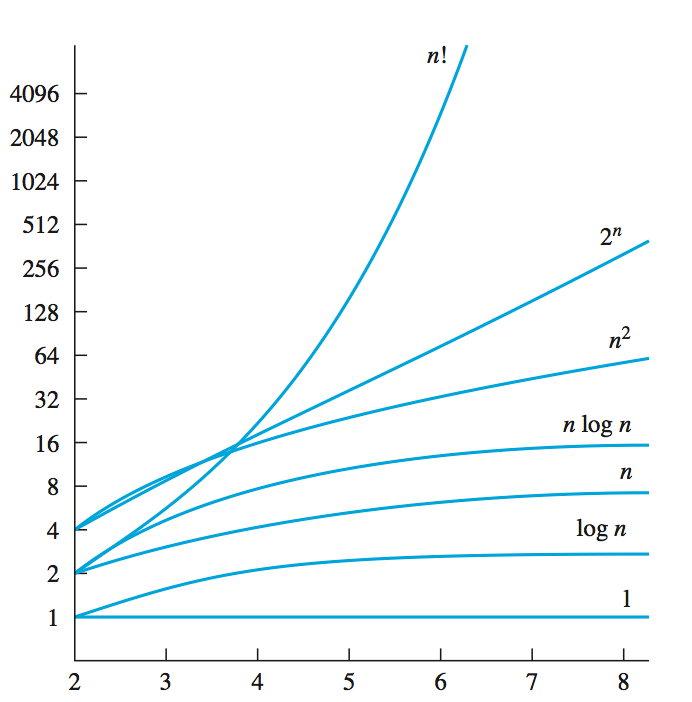
Running time of any algorithgm almost alway depent on
maount(size)of input taht it must process.- sorting 500 input take more time than 5 inputs .
-
when you comapre 2 function you need to look at the growth rate mean (n(input size) -> infinity)
- ex: f(n) =
-
10n^3 + 3n^2 -7,5n -1 <= 10n^3 + 3n^2 <= 10n^3 +3n^3 -
13n^3
-
10n^3 + 3n^2 -7,5n -1 is an element of O(n^3)
-
care about the upper bound(worst case scenario)
-
negative term in
big Oapproximation is usually ignore. -
GOal to classify function to one of these standard
big Oclassifycation
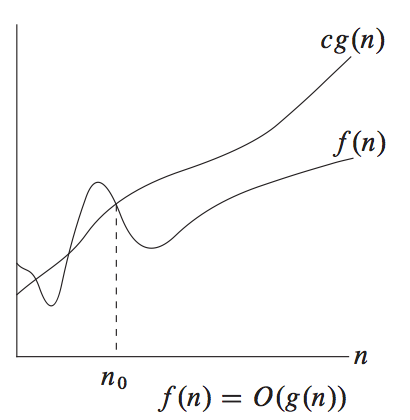
- Big O estimate: estimate the upper bound of your function.
- Upper bound give us the worst case scenario.
-
We alway want to over estimate to take the worst case scenerio to account.
f(n) is O(g(n))n^2 + 1 <= 2n^2when n >= 1
-
determine finding big O estimate mean finding multiplication(c) and threshold constant(k)
-
big O = upper Bound
-
big Omega = lower bound
-
Look at lecture note 28. for more example from page 29
-
ex:
- X^2 + 2X +1 <= X^2 + X^2 +X^2 = 3X^2
- thus: c = 3, k = 2 , so X^2 + 2X +1 is element of O(n^2)
- X^2 + 2X +1 <= X^2 + X^2 +X^2 = 3X^2
-
n! <= n^nfor c =1, k = 0 -
log(n^n) = nlog(n) = log(n.n.n.n.n.n.n.n.n) = log(n) + log(n) + log(n).... -
Book related The art of computer programming by Donald E. Knuth.
--------------Try in class exercise #2.
quiz next tuesday.
- parallel super computer develop at MIT
- Algorithm to live by braian christian book
- Bad sorting algorithm
- selection sort
- Insertion sort.
- Good sorting algorithm(nlogn)
- quick sort (recursive)
- merge sort )revursice)- O(nlog_2(n))
-
recurrence relation for a recursize algorithm
T(n) = C + T(n-1)- where T(n-1) is cost of display when input is
n-1recursive cost - base case: algorithm stop when n=0
CNon- recursive cost
-
T(n) = T(n/2) + 1- T(n) is the # of comparisons required to search for an element in a search sequence
size n - ex: merge sort algorithm split the list in to 2 list then it call 2 recursive call . we have
T(n) = 2T(n/2) + n
- T(n) is the # of comparisons required to search for an element in a search sequence
-
Binary Search: T(n) = T(n/2) + 1 -
Merge Sort: T(n) = 2T(n/2) + n
- the main tool we are using is
master theorem.
T(n) = aT(n/b) + f(n)
a: # of sub problem
n/b: size of each subproblem
f(n): Non-recursive cost
- use when a function is not fully explicit - ( T(n)=T(n*) + f(n) )
- ex:
- T(n)= 2T(n/4) * 12 n^(1/2) -7
- a: 2 , b : 4, d = 1/2
- T(n)= 2T(n/4) * 12 n^(1/2) -7
- Master theorem pitfall .
- T(n) is not monotone ( sin(x))
- if f(n) is not polonomial(2^n)
- b cannot express as a constant ( T(n) = T(n^(1/2))
- goal: give us undo operation
- use
last in first outtechnique - array is a random access data structure, where each element can access directly and in constant time
linked listis sequencetial access, you only know the start and end.
- Idea: build up a queue
stackis an ADT(abstract data type)- add from the back and pull from the back
bascially much like how data are stored in sql
- How do we build a stack?
- core Functionality:
Pushplace element on top of the stackPopRemove elements from the top of the stack(and return what you return)Peek- return the top of the stack.isEmpty
- core Functionality:
- Stack: implementation
- array base have zizequeue
- linked list does not have size
Java does provide implementation of stack
- Java collection:
java.util.Stack<E>
- add from the back pull from the front
- Insert at tail, pull out at head.
/* queue implementation
*
*/
public interface QueueInterface<AnyType> {
public void enqueue (AnyType e);
public AnyType dequeue();
public AnyType getFront();
public boolean isEmpty();
public void clear();
}- Java does haev queue implementation
java.util.Queue
- Application:
- Data stream. Data buffer.
-
design not base FIFO(FIrst in first out)
-
does allow line jumping or VIP service
-
there is a standard iplementation of priority in java via
PriorityQueue<E> -
when adding to priorityqueue thing will get order.
- therefore you can sort using this method.
- adding to
PriorityQueuetake nlogn - removing take
nlogntime
O(nlogn) as efficient as quick sort
-
when adding to a PriorityQueue and print out you will see that item is not order but actually it is. reason b/c that is it tree order. When you remove item and print out you will see that it is in order(refer to lecture note for more detail)
-
You need a
Comparatorto use priority queue -
jave implementation
java.util.PriorityQueue
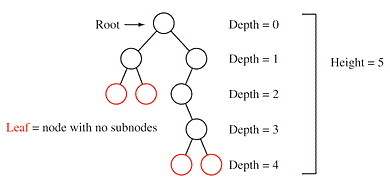
- layman: A tree is a graph(
Acylic graph) without a loop - A tree is a
collection of nodes(taht can hold keys,data,...)that are connected by edges- node with
no parentis the root - node with
no childrenis the leafconnected by exactly on unique path - all node are
- node with
- Why we deal with tree?
- we want to investigate the time-comoplexity Array, Linkedlist, Stack & queue
- Tree have potential of
nlog_2(n)efficiency for all operation( adding, removing)
- A tree s uch thhat all node have at most 2 children storing
1(true) ornull - for more exercise, look at lecture note.
- How to traverse the elements of a binary tree.
- explore level by level (from top to bottom, and from left to right) x
- Tree traversal
- Binary search with tree is
O(log_2(n) - for example, listing name of people in a company, one way you can do it is through a flat file. Or better: build it with a tree to create some hierarchy.
- idea: read every thing from the left of a node. then read itself. then read every thing on the right.
- Left < Root < right
- Call
tree walkor in order traversal. - Basic Operation with tree:
- Search
- MIn(walk through a tree at each choice pick left until no longer exist)
- max ( walk through a tree at each choice pick right until no longer choice.)
- insert
- delete
- Look at lecture note about BST for more info.
- when deleting: a leave will get deleted and thing you want to be deleted above it.
- What if you delete the main parent. SO delete then replace with
- Predessor
- Successor.
- BST is efficient if it is balance. Yes
we can guarantee the balanced structure of BST
/**
* In class Tree example
* Date: jun 29th, 2018
* this program is not fully done .
*/
//****************CompleteTree*******************/
public class CompleteTree{
private TreeNode root;
public completeTree{
this.root=null;
}
public CompleteTree(ArrayList<Integer> values){
//TODO: add to a tree from an array list
}
public void add(int newData){
TreeNode newNode = new TreeNode(newData);
if(this.root ==null){
this.root =newNode;
}else{
this.helperAdd(newNode);
}
}
private void helperAdd(TreeNode newNode, TreeNode currentRoot){// tell where in a tree each step, so you don't get loss
if(currentRoot.getLeftChild() == null){
currentRoot.setLeftChild(newNode);
}else if(currentRoot.getRightChild() == null)){
currentRoot.setRightChild(newNode);
}else{
//TODO: there is more stuff to thing about here.
}
}// END private helpAdd()
}// end COmpleteTree class
/********************SearchTree************************/
public class SearchTree{
public SearchTree(){
private TreeNode root;
public SearchTree{
this.root=null;
}
public SearchTree(ArrayList<Integer> values){
//TODO: add to a tree from an array list
}
public void add(int newData){
TreeNode newNode = new TreeNode(newData);
if(this.root ==null){
this.root =newNode;
}else{
this.helperAdd(newNode);
}
}// end add()
private void helperAdd(TreeNode newNode, TreeNode currentRoot){// tell where in a tree each step, so you don't get loss
//TODO: add or add recursively.
}// end SearchTree class
/** **********************TreeNode***************************/
public class TreeNode implements Comparable<TreeNode> {
private int data;
private TreeNode leftChild;
private TreeNode rightChild;
private TreeNode parent;
public TreeNode(int data){
this.data = data;
// you don't know the children when creating the node.
this.leftChild = null;
this.rightChild=null;
this.parent= null;
}
public TreeNode(int data, TreeNode parent){
this.data=data;
this.parent=parent;
this.leftChild = null;
this.rightChild=null;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(TreeNode other){
return (int) this.data.compareTo(other.getData());
}
//getter / setter for attribute. down here
}- goal: find node that match k.
- start at the root.
- at each node, compare k to key of node.
- if equal then return
- if k < key traverse the right child
- if k > key of U traverse the left child
- traverse until the tree is empty then it is not found.
- big O analysis:
O(d)d = depth
- make priority queue
- We perform priority search everyday; search for cheapest item,..
-
is an ADT
-
not base on FIFO
-
Enqueueaccording to it priority(not necessarily at the end of the line) -
dequeuereturn the highest priority -
Can be used to sort
-
use array,linkedlist,unbalance binary tree will be inefficient to build prority queue cause
O(n) -
if maintain binary tree balance we can perform operation in
O(log_2n) -
so we need to use heap priority item can be located
-
Heapis abinary treethat satisfies these Properties:- full or complete Binary tree
- if the last row is not full, all node are
full-to-the-left - every node has a key that is greater/smallerthan both of its children.(max heap)
-
Heapis optimal implementation of a prority queue -
page 12 lecture note for example
- we want to preserve the fulness of the tree.
- Let say you have a min-heap with root = 3. and you want to add 1 which is lower than the root. add to the children then swap it with above until 1 is the root.(heapify)
- php
- 1.B
- 2.B
- 3.A
- 4.A
- 5.C 'C%' start with C
- '%C' end with C
-
- C
-
- A
-
- A
- statement don't take runtime argument
- preparestatement take run time answer.
-
- B
-
-
- D
-
- A.
-
- D
-
- D
-
- B
-
- E
-
- C
-
- B
-
- C
-
- C.n-1
-
- C